Manufacturing Safety Audit Checklist: 7 Key Areas to Ensure Safety
In manufacturing, safety is the foundation of productivity and profitability. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reports over 2.7 million nonfatal workplace injuries and illnesses annually, with manufacturing consistently ranking among the highest-risk sectors. A robust safety audit is a proactive strategy to prevent costly incidents. This comprehensive manufacturing safety audit checklist provides a structured framework to identify vulnerabilities and reinforce a culture where every team member is a safety advocate.
A systematic approach embodies fundamental risk management principles, moving beyond compliance to proactive hazard control. By focusing on seven critical areas, you can transform your audit from a regulatory chore into a powerful tool for operational excellence.
This guide will walk you through an itemized checklist covering:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Compliance
- Machine Guarding and Lockout/Tagout (LOTO)
- Housekeeping and Workspace Organization
- Emergency Preparedness and Response
- Chemical Storage and Hazard Communication
- Incident Reporting and Investigation
- Ergonomics and Workplace Design
By implementing these checks, you can significantly reduce risks and protect your most valuable asset: your people.
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Compliance
The first checkpoint in any manufacturing safety audit checklist is a thorough review of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) compliance. A robust PPE program is the first line of defense against workplace injuries, directly shielding employees from chemical, physical, and mechanical dangers. The audit must ensure every worker is correctly equipped, trained, and consistently using the right PPE for specific tasks.
Proper compliance means verifying that all equipment meets or exceeds industry standards. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics confirms that a significant number of workplace injuries occur because employees were not wearing the required PPE. The audit must also confirm that PPE is stored correctly, regularly inspected, and replaced before it becomes ineffective.

Why It’s a Top Priority
Neglecting PPE compliance doesn’t just risk fines; it directly impacts worker safety and productivity. A well-managed PPE program demonstrates a company’s commitment to its workforce, fostering a stronger safety culture and reducing costly incidents. Companies like Toyota have successfully standardized PPE protocols, leading to measurable reductions in injury rates and associated downtime.
Actionable Audit Tips
To ensure your PPE program is effective, incorporate these specific actions into your audit process:
- Conduct Spot Checks: Perform random, unannounced checks across different shifts to get a true picture of daily compliance.
- Involve Your Team: Engage workers in the PPE selection process. When employees have a say in the comfort and fit of their equipment, they are more likely to wear it correctly.
- Use Visual Management: Implement visual aids, such as posters and color-coded charts, in each work area to clearly display the specific PPE required.
- Analyze Incident Data: Track and review all incidents and near-misses related to PPE. Use this data to identify trends and make targeted improvements to your safety protocols.
2. Machine Guarding and Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Systems
The second checkpoint in any manufacturing safety audit checklist is a rigorous evaluation of machine guarding and Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) systems. These protocols protect workers from hazardous energy and unexpected machine startups during maintenance. An audit must confirm that all points of operation are adequately guarded and that LOTO procedures are strictly followed to prevent catastrophic injuries.
Proper implementation involves ensuring every machine has the correct physical guards and safety devices. OSHA estimates that compliance with the LOTO standard prevents 120 fatalities and 50,000 injuries each year, making it a non-negotiable aspect of a safe manufacturing environment.

Why It’s a Top Priority
Failure to control hazardous energy is one of OSHA’s most frequently cited violations, resulting in severe fines and significant operational downtime. A robust LOTO and machine guarding program is a direct investment in worker well-being and operational continuity. Companies like General Motors have implemented comprehensive LOTO programs across over 180 facilities, drastically reducing energy-related incidents.
Actionable Audit Tips
To verify the effectiveness of your machine safety programs, integrate these specific actions into your audit:
- Create Visual LOTO Guides: Develop and post machine-specific, graphical LOTO procedures at each piece of equipment to simplify complex steps and reduce human error.
- Implement Color-Coded Locks: Assign different colored locks to specific departments or roles. This provides a quick visual cue of who is working on the equipment.
- Conduct Annual Verifications: Perform at least one annual inspection for each authorized employee to review and verify their understanding of the LOTO procedure.
- Track Near-Miss Incidents: Log and analyze all near-miss incidents related to machine guarding or failed LOTO to identify and correct system weaknesses before a serious incident occurs.
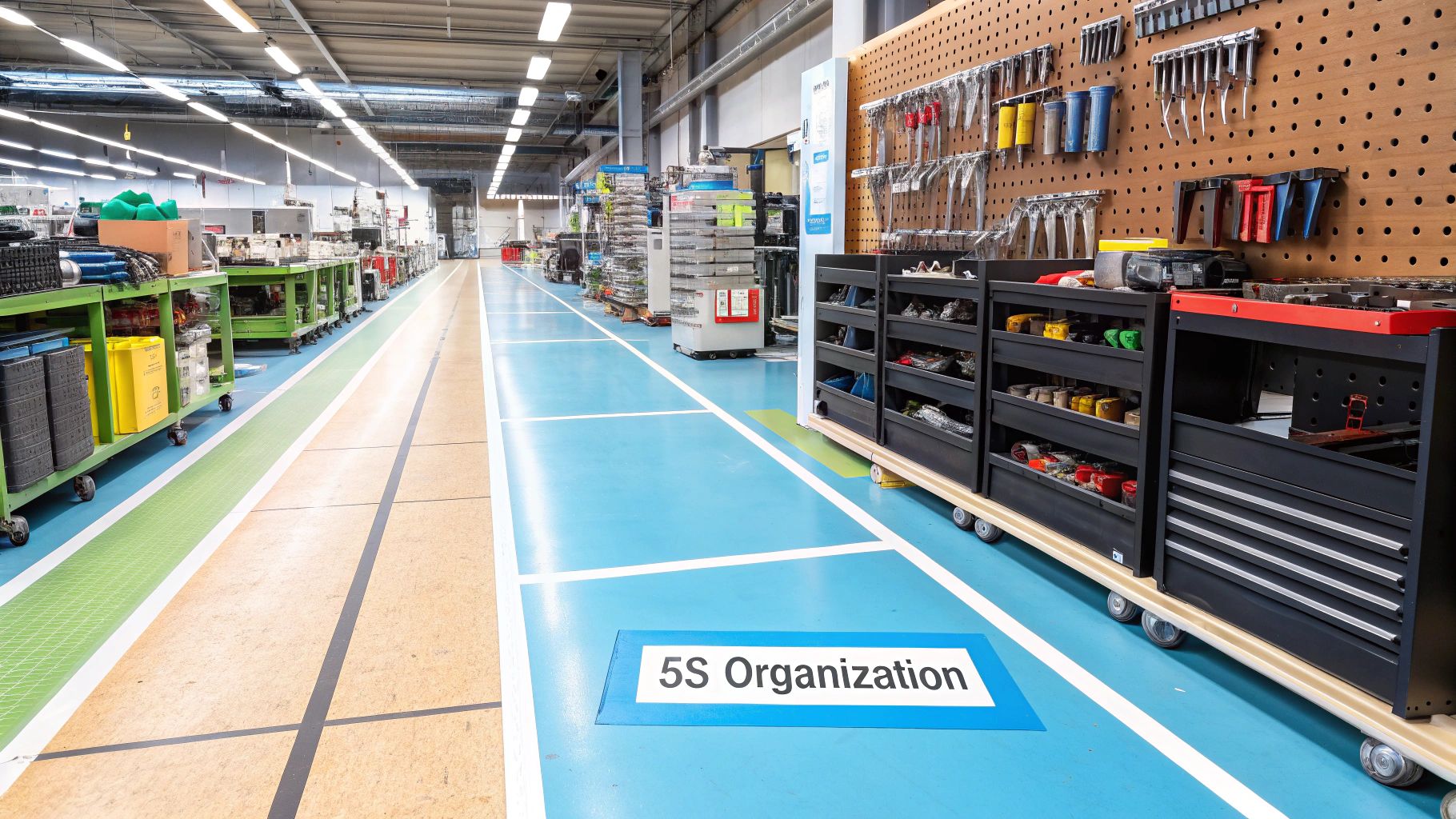
3. Housekeeping and Workspace Organization
A vital component of any manufacturing safety audit checklist is the evaluation of housekeeping and workspace organization. This involves ensuring every corner of the facility is clean, orderly, and free from hazards. Poor housekeeping is a direct contributor to accidents, and according to the National Safety Council, slips, trips, and falls are among the most common preventable injuries in a manufacturing setting.
Auditing this area means verifying clear and unobstructed walkways, ensuring floors are free of spills, and checking that tools are stored in designated locations. It also includes assessing waste management to prevent accumulations that could create fire hazards or obstruct emergency exits.

Why It’s a Top Priority
Excellent housekeeping directly correlates with enhanced safety and operational efficiency. An organized facility minimizes accident risks and reduces the time wasted searching for tools or materials, which boosts productivity. Companies like Toyota and Boeing have famously integrated 5S principles into their production systems, demonstrating a clear link between a meticulously organized workspace and a world-class safety record.
Actionable Audit Tips
To effectively assess and improve housekeeping in your facility, integrate these specific actions into your manufacturing safety audit checklist:
- Implement Red Tag Campaigns: Periodically conduct a “red tag” event where teams tag all unnecessary items, which are then moved to a holding area to be evaluated or discarded.
- Use Visual Management Tools: Employ shadow boards for tool storage and use floor markings to clearly define walkways, work zones, and storage areas.
- Establish Daily Inspection Routines: Create simple, visual checklists for each work area to be completed at the end of every shift, making housekeeping an integral part of daily work.
- Create Before-and-After Displays: Take photos of disorganized areas and display them next to photos of the same area after being organized. This visual proof reinforces standards and motivates teams.
4. Emergency Preparedness and Response Systems
A crucial component of any manufacturing safety audit checklist is the evaluation of emergency preparedness and response systems. This audit point assesses an organization’s readiness to handle crises such as fires, chemical spills, or medical emergencies. It involves a detailed review of evacuation procedures, emergency equipment, and communication protocols. A well-defined and regularly tested plan ensures swift, coordinated action that minimizes harm and limits operational disruption.
Proper preparedness means fire extinguishers, first aid stations, and eyewash stations are clearly marked, fully stocked, and regularly inspected. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), manufacturing facilities are a leading site for industrial fires, making robust response plans a non-negotiable aspect of operational safety.

Why It’s a Top Priority
A failure in emergency response can have catastrophic consequences. A well-drilled response system not only saves lives but also protects assets, reduces downtime, and upholds the company’s reputation. Companies like DuPont have established industry-leading emergency response protocols at their chemical plants, which serve as a benchmark for proactive crisis management.
Actionable Audit Tips
To ensure your emergency response plan is effective and reliable, integrate these specific actions into your audit:
- Conduct Unannounced Drills: Test your team’s real-world response capabilities by running surprise drills for various scenarios to expose gaps in training and communication.
- Use Tabletop Exercises: Gather key personnel to walk through decision-making processes for different emergency scenarios. This low-stakes environment is perfect for refining leadership roles and response strategies.
- Establish Mutual Aid Agreements: Form partnerships with neighboring facilities or local emergency services. These agreements provide critical backup resources if an incident exceeds your internal capacity.
- Create Pocket Cards: Distribute laminated, pocket-sized cards to all employees with essential information, such as emergency contact numbers and evacuation routes, for quick reference.
5. Chemical Storage and Hazard Communication
Another crucial component of any manufacturing safety audit checklist is an assessment of chemical storage and hazard communication. This involves a deep dive into how hazardous substances are stored, handled, and communicated throughout the facility. Proper management ensures employees are protected from exposure and spills are prevented.
An effective audit verifies compliance with standards like OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard. This includes ensuring all hazardous chemicals are properly labeled, Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are accessible, and workers are trained to understand them. OSHA consistently lists violations of this standard as one of its most frequently cited issues, underscoring its importance.
Why It’s a Top Priority
Failure to manage chemical hazards can lead to catastrophic accidents, severe health issues, and significant regulatory fines. A proactive chemical management system, like those implemented by companies such as BASF, not only ensures compliance but also builds a resilient safety culture. It minimizes the risk of costly incidents, protects the environment, and demonstrates a firm commitment to employee well-being. When auditing, consider specialized equipment, such as fast fueling systems that protect the environment, in mitigating risks like spills during transfer processes.
Actionable Audit Tips
To strengthen your chemical safety protocols, integrate these specific actions into your audit:
- Use Color-Coded Storage: Implement a visual system with color-coded areas for different chemical classes (e.g., flammables, corrosives) to prevent dangerous reactions from improper storage.
- Establish Regular SDS Reviews: Create a schedule to review and update your SDS library annually or whenever a new chemical is introduced. Ensure all employees know where to find them instantly.
- Implement Barcode Tracking: Use a barcode or QR code system to track chemical inventory. This helps monitor quantities, expiration dates, and locations.
- Provide Multilingual Support: In a diverse workforce, provide labels and training materials in multiple languages to ensure every employee fully understands the chemical hazards.
6. Incident Reporting and Investigation Systems
A crucial element of any manufacturing safety audit checklist is the evaluation of your incident reporting and investigation systems. This is a proactive framework for identifying, reporting, and learning from every workplace incident, including near misses. A world-class system establishes clear channels for reporting and ensures corrective actions are tracked to completion.
Effective systems move beyond blame-finding to uncover root causes. The audit must verify that reporting is easy and non-punitive. The National Safety Council states that for every serious injury, there are hundreds of near misses that go unreported. Tapping into this data is essential for identifying hazards before they result in a recordable incident.
Why It’s a Top Priority
A weak reporting system creates dangerous blind spots. When incidents and near misses go unreported, valuable learning opportunities are lost. A robust incident management process demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement and fosters a culture where every team member feels responsible for safety. Companies like DuPont have pioneered systems that empower employees to report observations, leading to a dramatic reduction in serious injuries.
Actionable Audit Tips
To ensure your reporting and investigation systems are driving real safety improvements, integrate these actions into your audit:
- Implement Anonymous Reporting: Provide channels, such as a secure digital portal, for employees to report concerns anonymously. This increases participation by removing fear of reprisal.
- Focus on Leading Indicators: Audit whether your system tracks proactive measures like safety observations and near-miss reports, not just lagging indicators like injury rates.
- Share Lessons Learned Widely: Ensure investigation findings are communicated across all relevant departments. Use storytelling in safety meetings to make the lessons memorable.
- Recognize Good Reporting: Create a program to celebrate and reward employees for active participation in reporting hazards and near misses. Positive reinforcement encourages a proactive safety culture.
7. Ergonomics and Workplace Design Assessment
A crucial component of a thorough manufacturing safety audit checklist is the evaluation of ergonomics and workplace design. This assessment focuses on how work tasks and workstation setups impact worker health over time. It involves a systematic review of repetitive motions and lifting procedures to prevent costly Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs).
Proper assessment means analyzing the fit between the worker and the environment to minimize strain and fatigue. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, MSDs are one of the leading causes of lost workday injuries. Auditing for ergonomic risks is a proactive measure to protect your workforce while enhancing productivity.
Why It’s a Top Priority
Neglecting ergonomics can lead to a gradual increase in worker compensation claims and absenteeism. An effective ergonomics program demonstrates a commitment to employee well-being, fostering a positive culture that translates into higher retention. For example, Ford Motor Company’s globally recognized ergonomics program has been credited with reducing employee injury rates by over 70%.
Actionable Audit Tips
To ensure your ergonomics and workplace design are optimized for safety, incorporate these specific actions into your audit:
- Involve Your Team: Actively engage employees in identifying ergonomic hazards and developing solutions. They offer invaluable frontline perspective on what causes discomfort.
- Use Job Rotation: Implement a structured job rotation schedule for tasks involving high levels of repetitive motion. This limits an individual’s exposure to specific strains.
- Provide Adjustable Equipment: Invest in adjustable workstations, chairs, and tools wherever possible. Allowing workers to customize their setup is one of the most effective ergonomic controls.
- Track Early Reports: Create a system for employees to report early signs of discomfort, like soreness or fatigue, without fear of reprisal. Addressing these minor issues promptly can prevent them from becoming serious MSDs.
7-Point Manufacturing Safety Audit Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity (🔄) | Resource Requirements (⚡) | Expected Outcomes (⭐📊) | Ideal Use Cases (💡) | Key Advantages (⭐) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Compliance | Moderate to High: ongoing training & audits 🔄 | Medium: equipment costs, maintenance, training ⚡ | Reduces injuries, ensures compliance, lowers insurance costs ⭐📊 | Workplaces with physical hazards, regulated industries 💡 | Direct injury reduction, regulatory compliance ⭐ |
| Machine Guarding and Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Systems | High: complex setup, documentation, training 🔄 | High: locks/tags, training, inspections ⚡ | Prevents severe machinery injuries, systematic safety ⭐📊 | Facilities with heavy machinery and energy risks 💡 | Prevents serious injuries, legal requirement ⭐ |
| Housekeeping and Workspace Organization | Moderate: discipline and cultural change 🔄 | Low to Medium: organizational tools, time ⚡ | Reduces slips/falls, improves productivity, morale ⭐📊 | General workplaces focusing on safety and efficiency 💡 | Improves safety and efficiency, reduces hazards ⭐ |
| Emergency Preparedness and Response Systems | High: coordination, drills, equipment 🔄 | Medium to High: training, equipment, drills ⚡ | Saves lives, reduces damage, builds trust ⭐📊 | Any organization needing disaster/emergency readiness 💡 | Life-saving, compliance, liability reduction ⭐ |
| Chemical Storage and Hazard Communication | High: regulatory compliance, training 🔄 | Medium to High: storage, ventilation, training ⚡ | Prevents exposures, reduces fines, protects reputation ⭐📊 | Facilities handling hazardous chemicals 💡 | Exposure prevention, regulatory compliance ⭐ |
| Incident Reporting and Investigation Systems | High: culture change, investigation process 🔄 | Medium: training, investigation time ⚡ | Proactive hazard ID, improved safety culture ⭐📊 | All workplaces seeking continuous safety improvement 💡 | Reduces repeat incidents, improves culture ⭐ |
| Ergonomics and Workplace Design Assessment | Moderate to High: assessments, redesign 🔄 | Medium to High: ergonomic equipment, experts ⚡ | Reduces musculoskeletal disorders, boosts productivity ⭐📊 | Work environments with repetitive or physical tasks 💡 | Reduces injuries, enhances satisfaction ⭐ |
Turning Your Safety Audit into a Competitive Advantage
Completing a comprehensive manufacturing safety audit checklist is a significant accomplishment, but its true value is realized in the actions that follow. The checklist items we’ve detailed are interconnected components of a holistic safety culture that directly impacts operational excellence.
Viewing safety through this lens reveals its connection to productivity and profitability. The National Safety Council estimates the total cost of work injuries in 2021 was a staggering $167 billion. Each near-miss prevented and each ergonomic adjustment made is a direct investment in your people. This commitment reduces costly incidents, minimizes downtime, and lowers insurance premiums.
From Checklist to Culture: The Path Forward
The transition from a static checklist to a dynamic safety program requires a commitment to continuous improvement. Your audit findings provide a clear roadmap.
- Prioritize and Act: Use a risk-based approach to prioritize the most critical findings. Assign clear ownership, set realistic deadlines, and track progress.
- Empower Your Team: A strong safety culture is built from the ground up. Involve employees in developing solutions, as they have the most practical insights into potential hazards.
- Leverage Technology: Modern tools can automate and streamline safety processes. Digital systems can manage training records, track incidents, and ensure accountability.
The Overlooked Element: Managing On-Site Personnel
A critical aspect of a robust safety program is managing the flow of non-employees through your facility. Contractors, suppliers, and visitors can introduce significant risk if not managed properly. They may be unfamiliar with your specific LOTO procedures, emergency evacuation routes, or PPE requirements.
This is where a modern visitor management system becomes an indispensable part of your safety infrastructure. The benefit of such a system is its ability to actively reinforce your safety protocols. You can ensure every contractor completes a digital safety induction and acknowledges site-specific hazards before they are granted access. During an emergency, having a real-time, accurate list of every individual on-site is a critical life-safety function that dramatically improves evacuation efficiency. By integrating this control layer, you extend your safety culture to everyone who walks through your doors, turning a potential vulnerability into a managed process. This proactive approach elevates your safety program and strengthens your competitive advantage.
Ready to transform your facility’s safety and compliance from a manual checklist to an automated, intelligent system? Discover how VisitUs can integrate seamless visitor and contractor management into your safety protocols, ensuring everyone on-site is inducted, accounted for, and safe. Learn more and book a demonstration at VisitUs.