Top Evacuation Plans Examples to Protect Your Industry
Most organisations believe they're prepared for an emergency, but the statistics tell a different story. A shocking 75% of businesses without a comprehensive emergency plan fail within three years of a disaster. Having an effective evacuation plan isn’t just about compliance; it's about ensuring your organization can recover and protecting your most valuable asset: your people. A generic, one-page document simply won't suffice when faced with a crisis, from a factory fire to an extreme weather event. The difference between a controlled exit and a catastrophic failure lies in the details.
This guide moves beyond basic templates to provide a strategic breakdown of 8 distinct evacuation plans examples from diverse sectors. We will analyze the specific tactics that make these plans effective, offering actionable takeaways you can apply to your own procedures. For a broader understanding of organizational readiness, exploring wider strategies for natural disaster preparedness can provide valuable context.
Furthermore, we'll explore why a modern visitor management system is critical for a successful evacuation. Instead of just tracking who enters, these systems deliver the immense benefit of real-time data, allowing you to instantly and accurately account for every person on-site—staff, visitors, and contractors. This capability transforms a chaotic evacuation into an organized, safe procedure, providing certainty when it matters most.
1. Fire Emergency Evacuation Plan (FEEP)
A Fire Emergency Evacuation Plan (FEEP) is a foundational safety document, legally mandated for most commercial and public buildings. Its purpose is to provide a systematic procedure for the safe and orderly evacuation of occupants during a fire. This plan is crucial for creating a predictable response in a chaotic situation, which studies show can reduce evacuation times by up to 50% and significantly lower the risk of injury or fatality.
The core of a FEEP involves mapping out primary and secondary escape routes, establishing clearly marked assembly points away from the building, and defining the roles of key personnel like fire wardens. Historical events, such as the MGM Grand Hotel fire in 1980, tragically demonstrated the importance of these plans, leading to sweeping reforms in fire safety standards. A robust FEEP is a non-negotiable component of workplace health and safety.
Strategic Breakdown and Actionable Takeaways
Effective FEEPs are dynamic documents, not static posters. Their success hinges on regular training, clear communication, and defined responsibilities. By implementing a visitor management system, your organization gains the benefit of an instant, accurate list of all on-site personnel. This eliminates dangerous guesswork, ensuring everyone is accounted for during an emergency and providing first responders with critical, life-saving information.
Key Tactics for Implementation:
- Assign & Train Wardens: Designate and thoroughly train fire wardens for each floor or department. Their duties include guiding personnel, assisting individuals with mobility issues, and performing a final sweep of their area.
- Conduct Regular Drills: Schedule and conduct comprehensive fire drills at least twice a year. This practice builds muscle memory and reveals potential flaws in the plan. Analysing the outcomes of previous drills can offer valuable insights; you can learn more about reviewing past evacuation data.
- Maintain Clear Routes: Ensure all designated evacuation paths, including corridors and stairwells, are kept clear of obstructions at all times. Regular inspections are vital.
The following infographic illustrates the fundamental process flow of a personal evacuation during a fire alarm.
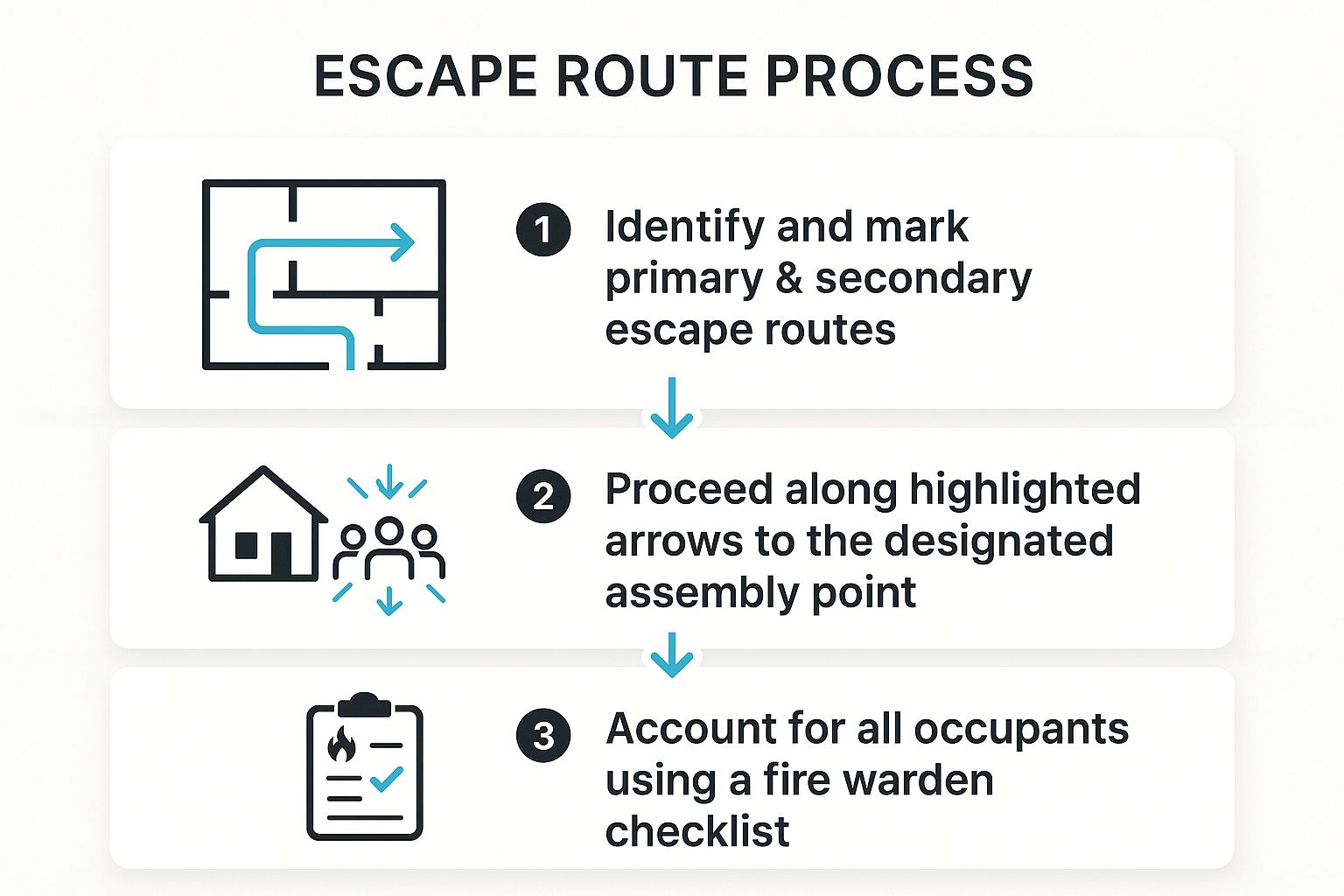
This visual process underscores the importance of a clear, sequential response, moving from awareness (identifying routes) to action (evacuating) and finally to verification (headcount), which is a core principle of effective evacuation plans examples.
2. Hurricane/Severe Weather Evacuation Plan
A Hurricane or Severe Weather Evacuation Plan is a large-scale strategy for moving populations from high-risk zones to safer locations ahead of a catastrophic event. Unlike a single-building plan, this type involves multiple government agencies coordinating transport, shelter, and public communication. These plans are vital for coastal and tornado-prone regions where staying in place is not a viable option.
The response to Hurricane Katrina in 2005, which led to over 1,800 fatalities, drastically reformed emergency management, emphasizing proactive coordination. In contrast, the pre-emptive evacuation of 6.8 million Floridians for Hurricane Irma in 2017 showcased the life-saving potential of a well-organized logistical operation. Such evacuation plans examples demonstrate that an effective severe weather response is a critical public safety function.

Strategic Breakdown and Actionable Takeaways
Successful severe weather plans depend on clear communication channels, pre-staged resources, and public compliance. For organizations, having an internal plan that aligns with the regional strategy is crucial. A modern visitor management system provides the benefit of an instant roll call, allowing you to account for every staff member, contractor, and visitor. This is critical when a site-wide shutdown is ordered with little notice, ensuring no one is left unaccounted for.
Key Tactics for Implementation:
- Know Your Zone & Routes: Identify your official evacuation zone and map out primary and alternate escape routes well before a storm warning. Share this information with all staff.
- Prepare a 'Go-Bag': Encourage employees to have a personal emergency kit ready. For the business, prepare a 'go-bag' with critical documents, data backups, and contact lists.
- Plan for Special Needs: Identify personnel or clients (especially in aged care) who require assistance. Coordinate with local emergency services to register their needs in advance, ensuring they receive priority support.
3. Active Shooter/Lockdown Evacuation Plan
An Active Shooter/Lockdown Evacuation Plan is a modern security protocol designed for violent intruder events. This plan is based on the widely adopted 'Run, Hide, Fight' methodology, empowering individuals to make life-saving decisions based on their immediate situation. It prioritizes escaping when a safe path is available, securing in place when it is not, and, as a last resort, taking action to disrupt the threat.
The tragic events at Virginia Tech in 2007 and Sandy Hook Elementary in 2012 served as major catalysts for the widespread adoption of these dynamic plans in schools and workplaces. Research by the FBI shows that nearly 70% of active shooter incidents are over in less than five minutes, underscoring the critical need for procedures that empower immediate, decisive action. A well-rehearsed active shooter plan is a vital component of modern organizational safety.
Strategic Breakdown and Actionable Takeaways
An effective active shooter plan is not about a single response but a flexible set of options. In these high-stakes situations, an automated visitor management system provides the invaluable benefit of an instant, real-time list of all on-site personnel. This gives first responders accurate information to work with, preventing them from wasting critical time searching for individuals who are not on-site and allowing them to focus on neutralizing the threat.
Key Tactics for Implementation:
- Embrace Dynamic Training: Conduct regular scenario-based drills that practice all three components: Run, Hide, and Fight. This builds critical thinking skills, allowing personnel to assess and react to a developing situation.
- Establish Secure Zones: Identify and pre-designate 'hard corners' or secure rooms that can be effectively barricaded. Ensure these locations are known to all staff. For educational institutions, leveraging technology eligible for proactive school violence prevention programs can be a critical enhancement.
- Coordinate with First Responders: Liaise with local law enforcement to understand their response protocols. Share floor plans and key information to facilitate a faster and more effective intervention.
The following video from the Department of Homeland Security provides a clear overview of the "Run, Hide, Fight" protocol in an active shooter situation.
This video highlights the core principles of situational awareness and decisive action, which are foundational to the modern evacuation plans examples developed for active threat incidents.
4. Hospital/Healthcare Facility Evacuation Plan
A Hospital or Healthcare Facility Evacuation Plan is a highly specialized protocol designed for environments where a significant portion of occupants cannot self-evacuate. This plan addresses the immense challenge of moving patients who may be non-ambulatory, connected to life-support equipment, or in critical condition. It prioritizes a phased approach, often starting with horizontal evacuation (moving patients to a safer fire compartment on the same floor) before progressing to full facility evacuation.
The complexity of these plans was starkly illustrated during Hurricane Sandy in 2012, where New York hospitals successfully evacuated hundreds of patients amidst power failures. These events highlight that a healthcare evacuation plan is one of the most intricate examples of emergency preparedness. The primary goal is to maintain patient care and safety under extreme duress, where patient mortality rates can increase by over 25% during unplanned evacuations.
Strategic Breakdown and Actionable Takeaways
An effective hospital evacuation plan is a scalable, tiered response. Success is contingent on intense, repetitive staff training and the immediate availability of specialized equipment. Integrating a visitor management system is crucial. It delivers the benefit of an instant, accurate manifest of all non-clinical personnel on-site, such as family members and contractors. This ensures a complete and verifiable headcount, preventing dangerous delays and confusion during an evacuation.
Key Tactics for Implementation:
- Prioritize & Tag Patients: Develop a clear triage system to tag patients with evacuation priority levels (e.g., ambulatory, wheelchair-bound, bed-ridden) at the onset of an emergency to allocate resources efficiently.
- Stage & Maintain Equipment: Pre-position and regularly inspect evacuation equipment like patient sleds, transfer sheets, and evacuation chairs in designated, accessible locations on every floor. Ensure all critical medical equipment has fully charged battery backups.
- Conduct Phased Drills: Regularly practice horizontal evacuation drills, as this is the most common first step. Training should involve hands-on use of equipment and focus on techniques for safely moving non-ambulatory patients, which is a key part of workplace emergency procedures.
5. Nuclear Power Plant Emergency Evacuation Plan
A Nuclear Power Plant Emergency Evacuation Plan is a large-scale, multi-agency strategy to protect the public from radiation exposure. These highly detailed plans are a legal necessity for communities surrounding nuclear facilities, providing a framework for notification, sheltering, and evacuation. The plan’s core function is to mitigate risk in a low-probability, high-consequence scenario.
These plans are organized around designated Emergency Planning Zones (EPZs), typically a 16-kilometer radius for airborne plume exposure. Historical events like the Fukushima Daiichi disaster in 2011, which prompted the evacuation of 154,000 people, underscore the critical need for these pre-emptive strategies. Well-rehearsed nuclear evacuation plans are among the most complex yet essential examples of public safety coordination.
Strategic Breakdown and Actionable Takeaways
An effective nuclear emergency plan hinges on rapid communication and seamless coordination between facility operators and government agencies. Its success is measured by the ability to quickly move large populations out of harm's way. For nearby organizations, integrating their site plans with the public one is critical for safety and accountability.
Key Tactics for Implementation:
- Know Your Zone: Identify your home and workplace's specific Emergency Planning Zone and designated evacuation route. This information is typically provided annually by your local council or energy provider.
- Establish Clear Communication Protocols: Determine how your organization will receive and disseminate official alerts. A modern visitor management system offers the benefit of instantly broadcasting emergency notifications to everyone on-site, ensuring clear and consistent instructions.
- Prepare for Multiple Scenarios: Develop procedures for both evacuation and shelter-in-place orders. Ensure your emergency kits are stocked with essentials like water, non-perishable food, and any necessary medications to last several days.
6. Wildfire Evacuation Plan
A Wildfire Evacuation Plan is a specialized strategy for communities in the Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI), where development meets fire-prone wildland. This plan must account for rapidly shifting fire fronts, potential road closures, and widespread infrastructure failure. It prioritizes proactive measures, such as creating defensible space around properties and encouraging early evacuation to prevent last-minute panic.

The necessity of these plans has been tragically underscored by events like the 2018 Camp Fire in California, which caused 85 fatalities and highlighted catastrophic evacuation challenges. With climate change extending and intensifying fire seasons globally—the average number of high-risk fire weather days has increased by 54% since the 1980s—a well-rehearsed Wildfire Evacuation Plan is a critical survival tool.
Strategic Breakdown and Actionable Takeaways
Effective wildfire plans are built on community-wide preparedness and individual responsibility, shifting the focus from reactive escape to proactive readiness. Organizations in at-risk areas benefit greatly from a visitor management system. It provides a real-time log of all personnel, ensuring no one is left behind when an evacuation order is issued and that everyone can be accounted for safely and efficiently.
Key Tactics for Implementation:
- Plan & Practice Routes: Identify at least two distinct evacuation routes from your home or workplace. Drive them at different times of the day to understand potential traffic choke points and alternate paths.
- Create Defensible Space: Follow guidelines from programs like the NFPA's Firewise USA to clear a buffer zone of at least 30 meters around your property by removing flammable vegetation and materials.
- Prepare a "Go-Bag": Assemble an emergency kit with essentials like N95 masks, water, non-perishable food, medications, important documents, and a battery-powered radio. During fire season, keep your vehicle fueled and parked facing the direction of escape.
7. School Emergency Evacuation and Reunification Plan
A School Emergency Evacuation and Reunification Plan is a specialized safety protocol that goes beyond simple building evacuation to manage the complex process of safely reuniting students with their authorized guardians after an incident. This plan addresses the unique vulnerabilities of children and the legal necessity of supervised care, preparing for threats from fires to active assailant situations.
The need for such comprehensive plans was tragically underscored by events like the Sandy Hook Elementary tragedy in 2012, which led to significant advancements in reunification protocols. A well-organized reunification process is a non-negotiable part of modern school safety. It maintains order in a high-stress environment and ensures every child is accounted for and released securely.
Strategic Breakdown and Actionable Takeaways
An effective school plan is built on clear roles, constant communication, and meticulous record-keeping. Integrating a visitor management system is crucial, delivering the benefit of an instant, accurate digital roll call of every person on campus—staff, students, volunteers, and contractors. This ensures no one is overlooked and that reunification data is precise, providing peace of mind to parents and authorities.
Key Tactics for Implementation:
- Establish a Reunification Site: Designate a primary and secondary off-site location for reunification. This location should be secure and separate from the immediate incident area to ensure a controlled process.
- Practice Multiple Drill Types: Conduct regular, varied drills covering fire, lockdown, and shelter-in-place scenarios. This diverse practice ensures the school community is prepared for any contingency. Comprehensive training is the backbone of any successful plan; you can discover more about building an effective evacuation training plan.
- Define Clear Roles: Assign specific roles to staff members for the evacuation and reunification phases (e.g., student runners, accountability officers, parent check-in, student release). This division of labor prevents confusion and speeds up the process.
8. Chemical Plant/Industrial Facility Evacuation Plan (Shelter-in-Place)
An industrial facility evacuation plan addresses incidents involving hazardous materials, such as toxic chemical releases. Unlike standard evacuations that direct people outside, these plans often prioritize a "shelter-in-place" strategy. This is because moving outdoors could expose individuals to airborne contaminants, making it safer to remain inside a sealed building until the threat has passed. These plans are heavily regulated by bodies like OSHA and the EPA.
The need for such specialized plans was tragically underscored by the 1984 Bhopal disaster in India, which led to sweeping global reforms in industrial safety. Data shows that a properly executed shelter-in-place can reduce a person's exposure to hazardous chemicals by over 80%. A well-executed shelter-in-place procedure is a vital public safety measure for any community near industrial operations.
Strategic Breakdown and Actionable Takeaways
The success of a shelter-in-place plan depends on rapid communication and public education. For businesses in proximity, a visitor management system is critical. It provides the benefit of an instant and accurate roll call to confirm that all staff, contractors, and visitors are safely accounted for inside the facility. This eliminates uncertainty and allows safety managers to focus on securing the building.
Key Tactics for Implementation:
- Establish Clear Protocols: Designate an interior room with few windows as a shelter area. Pre-stock it with supplies like plastic sheeting and duct tape to seal doors, windows, and vents.
- Implement Mass Notification: Utilize a multi-channel emergency notification system to alert staff and the surrounding community. Instructions should be clear: shelter-in-place, turn off all HVAC systems, and tune into local emergency broadcasts.
- Conduct Joint Drills: Regularly practice shelter-in-place drills in coordination with local first responders and neighboring businesses. This identifies communication gaps and ensures procedures are effective before a real crisis occurs.
8 Emergency Evacuation Plans Comparison
| Plan Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fire Emergency Evacuation Plan (FEEP) | Moderate – requires regular updates and training | Moderate – signage, alarms, staffing | High – reduces casualties and confusion | Commercial/public buildings, offices, schools | Legally required, standardized protocols |
| Hurricane/Severe Weather Evacuation Plan | High – multi-agency coordination, advance warning needed | High – transportation, shelters | Very High – saves thousands, reduces congestion | Coastal/ hurricane-prone regions, communities | Organized routing, protects vulnerable populations |
| Active Shooter/Lockdown Evacuation Plan | High – complex decision framework, frequent training | Low to Moderate – training, communication | Moderate to High – increases survival rates | Schools, workplaces, public venues | Flexible, empowers individual decision-making |
| Hospital/Healthcare Facility Evacuation Plan | Very High – specialized equipment and extensive staff training | Very High – medical equipment, staffing | High – protects vulnerable patients | Hospitals, healthcare facilities | Protects critically ill, role clarity |
| Nuclear Power Plant Emergency Evacuation Plan | Very High – multi-agency, detailed planning and drills | High – alert systems, KI distribution | High – protects against radiation exposure | Communities near nuclear plants | Regular testing, multi-layered protective actions |
| Wildfire Evacuation Plan | Moderate to High – dynamic conditions, tiered warnings | Moderate – alerts, evacuation logistics | High – reduces loss of life and property damage | Fire-prone rural/urban interface areas | Early warning system, community preparedness |
| School Emergency Evacuation & Reunification | High – multi-threats, legal considerations, coordination | Moderate – staff, communication systems | High – ensures child safety and accountability | Educational institutions | Ensures accountability, multi-hazard approach |
| Chemical Plant/Industrial Shelter-in-Place | High – complex hazard management, shelter protocols | Moderate to High – detection, alerts | Moderate to High – prevents chemical exposure | Communities near chemical/industrial plants | Shelter often safer than evacuation, quick notification |
From Plan to Practice: Activating a Safer Tomorrow
Throughout this guide, we have explored a diverse range of evacuation plans examples, from a factory fire response to a complex healthcare facility evacuation. While each plan is uniquely tailored to its environment, a powerful, unifying theme has emerged: the critical importance of adaptable, well-rehearsed, and data-driven strategies.
Effective plans are not static documents; they are living frameworks that evolve. They recognize that different emergencies demand different responses. The key takeaway is that preparation moves beyond mere compliance. It involves understanding your specific vulnerabilities, establishing clear communication channels, and empowering individuals to act decisively under pressure.
The Unseen Gap: From Roll Call to Rescue
A recurring challenge across all scenarios is the chaotic and often inaccurate process of accounting for every person on-site. Traditional paper sign-in sheets are notoriously unreliable. Emergency services data shows that up to 30% of response time can be lost trying to confirm if everyone has safely evacuated. This critical gap is where a modern, automated system transforms your evacuation plan from theoretical to practical.
By integrating a visitor management system, you gain the benefit of an accurate, real-time digital roll call accessible from any mobile device. This provides certainty in a crisis. First responders no longer have to second-guess their information or risk lives searching for someone who was never there. Instead, they receive a definitive list of all staff, visitors, and contractors, allowing them to focus their efforts where they are needed most. This automated accuracy demonstrates a profound commitment to the safety of every individual in your care.
Activating Your Plan with Confidence
The evacuation plans examples we've analyzed prove that the ultimate goal is to build resilience. This is achieved by embedding a plan into your culture through regular drills and leveraging technology that supports swift, intelligent action. By prioritizing clarity, defining roles, and ensuring you have an accurate, real-time headcount, you transition from simply having a plan to having a true emergency response capability. This proactive stance provides peace of mind, protects your people, and ensures your organization is prepared to act with confidence when it matters most.
Ready to close the critical safety gap in your evacuation plan? Discover how VisitUs provides instant, accurate roll calls during emergencies, empowering your fire wardens and first responders with the real-time data they need. VisitUs transforms your evacuation strategy from a document into a dynamic, life-saving tool.





